Maybe heard of it before, but ethyl vinyl acetate (EVA) is where many everyday manufacturing and segments of industry differentiate. Here are some hidden secrets of this hero. EVA is widely used in various fields such as films, coating materials, foams, shoes, adhesives, photovoltaic modules, cables and drug delivery systems.
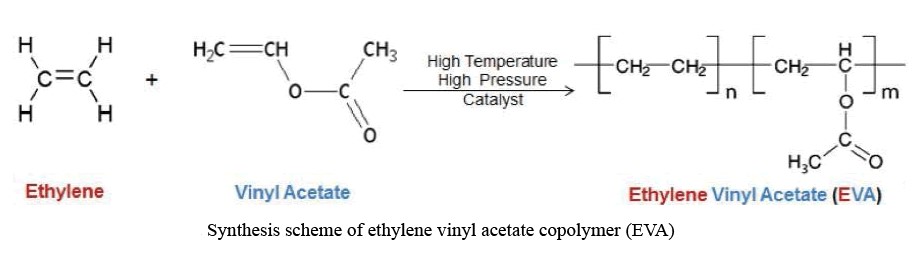
What is Ethyl Vinyl Acetate (EVA)? EVA is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate with the structure shown below.
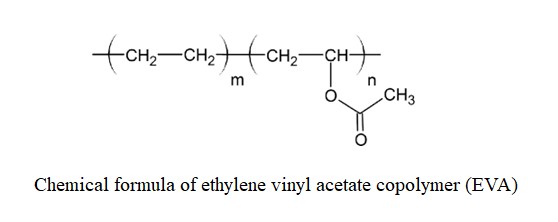
The large majority of the copolymer's weight percentage is ethylene and the vinyl acetate composition tends to vary between 10-40%. Ethylene and vinyl acetate here are called co-monomers of the main EVA copolymer chain. The physical properties of EVA can also be tuned by adding pigments or varying the average molecular weight through copolymerization with other monomers.
It is an extremely elastic and durable thermoplastic with excellent clarity, gloss and low odor. EVA has many attractive properties, such as excellent adhesion to many polar and non-porous substrates at low cost, good flex-crack and puncture resistance, as well as good hot tack and heat bonding.
EVA behaves like thermoplastics and flexible plastics depending on the amount of vinyl acetate within composition. EVA with a higher vinyl acetate content has a lower solid amorphous content and is responsible for a higher flexibility. Higher process temperatures aid the extrusion process by reducing the flow viscosity of polymers with lower vinyl acetate content. Vinyl acetate content plays an important role in the solubility, crystallinity, flexibility and porosity of extruded EVA.
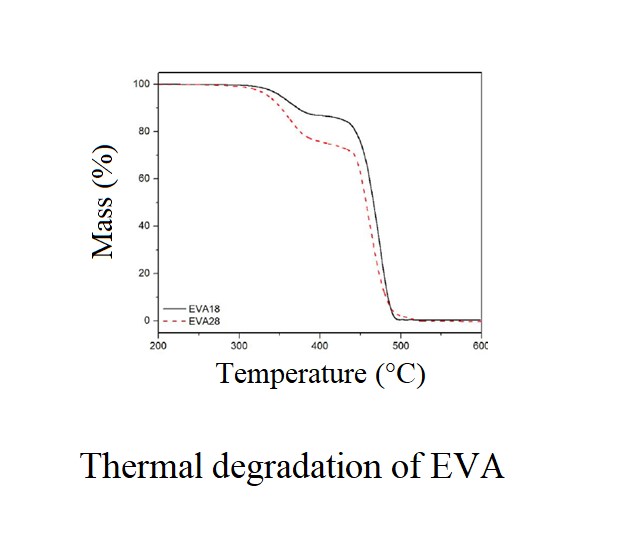
EVA is proven to be stable at elevated processing temperatures by thermogravimetric analysis because decomposition of EVA starts above 250°C.